Blog & Latest Updates
Fly Fishing Articles
Insects by Common Name


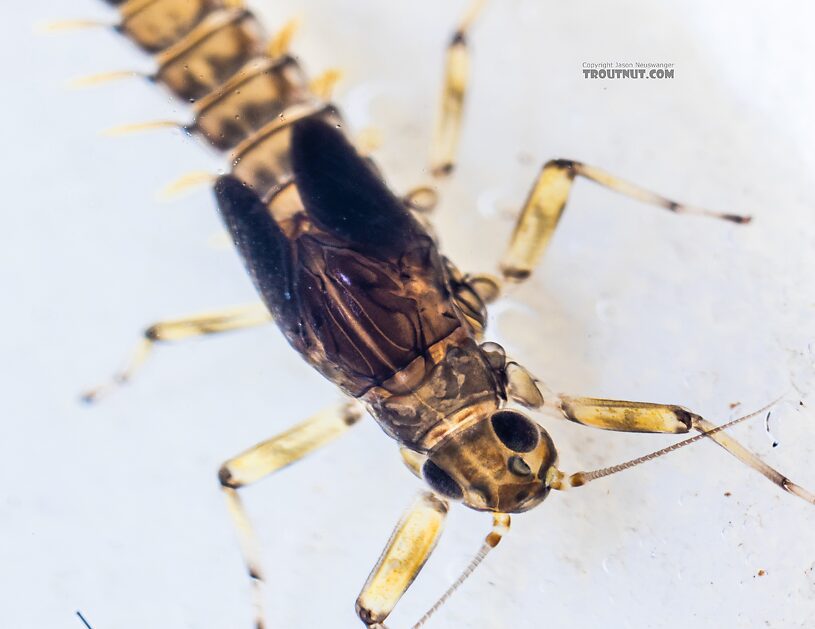
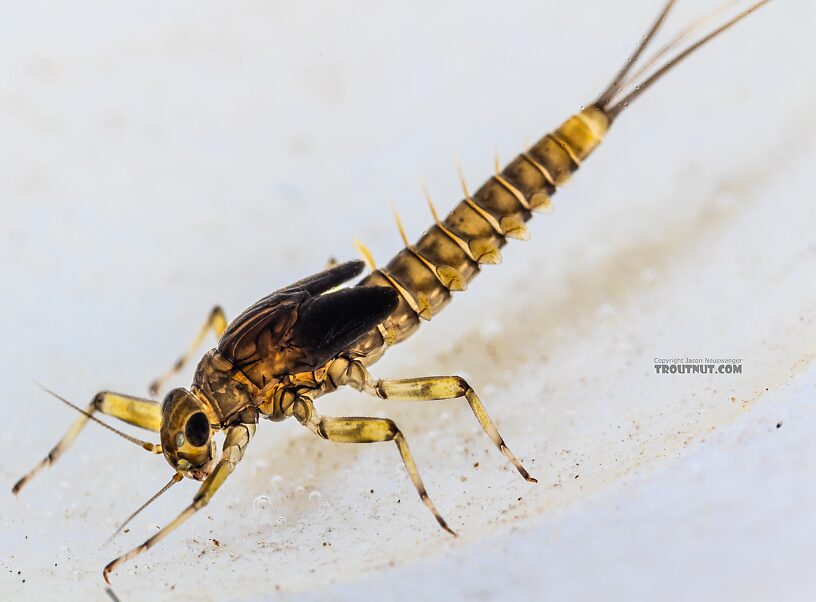
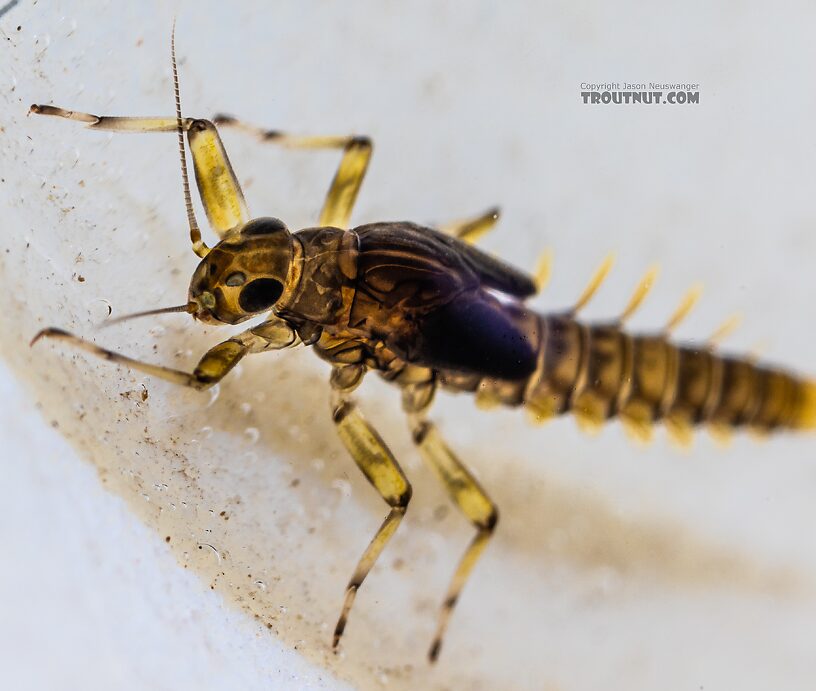
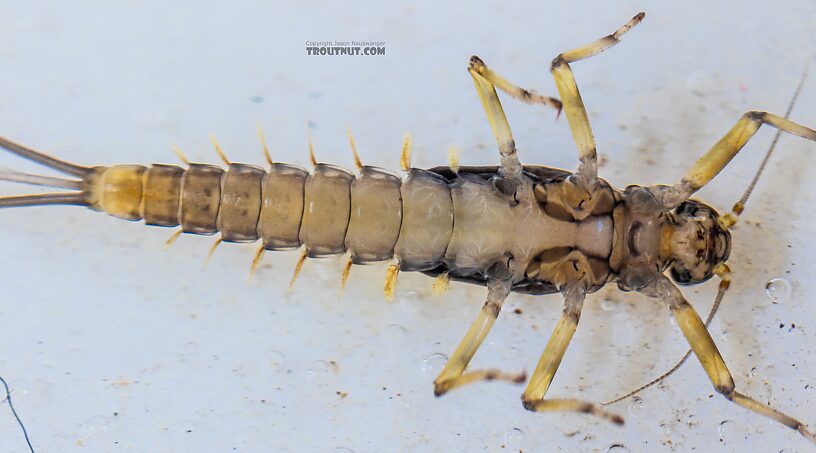
Baetis tricaudatus (Blue-Winged Olive) Mayfly Nymph Pictures
Classification
Kingdom
Animalia (Animals)
» Phylum
Arthropoda (Arthropods)
» Class
Insecta (Insects)
» Order
Ephemeroptera (Mayflies)
» Family
Baetidae (Blue-Winged Olives)
» Genus
Baetis (Blue-Winged Olives)
» Species
tricaudatus (Blue-Winged Olive)
A nymph of the same species as this one emerged into a dun in my studio so I got photos of both stages.
NOTE: I missed an important key characteristic the first time I tried to identify this one (robust setae (Seta: Little hairs on insects.) on the abdominal sternites (

One sternite of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.
However, I'm leaving the flawed analysis below with this disclaimer, because some aspects of how I approached that dead end might be informative in the future.
----Incorrect analysis below----
After spending a lot of time with this one under my shiny new microscope, I'm still not quite sure what it is. I botched my attempt to expose the mouth parts that might make the ID more definitive. Based on the key in Webb et al 2018's "Baetis Larvae of North America," here's my reasoning at each key couplet.
Couplet 1. The pronotum (Pronotum: The top of the insect prothorax.) lacks dark, submedian U-shaped markings. Also, if I were to follow through to couplet 2, there seem to be characteristics that rule out each of the options: the intercalaris complex is ruled out by the abdominal markings, and the caudal (Caudal: Toward the posterior tip of the body.) filaments have neither a dark median band (ruling out the flavistriga complex) nor uniform pale coloration (ruling out Baetis notos). This sends me with decent confidence to couplet 4.
Couplet 4. I cannot find robust setae (Seta: Little hairs on insects.) in my microscope on the scapes, pedicels, paraprocts, or sterna. I also do not see a pair of dark, bilobed markings on the pronotum (Pronotum: The top of the insect prothorax.). Unless I overlooked these characteristics, proceed to couplet 9.
Couplet 9. Abdominal tergum (Tergum: the dorsal part of an abdominal segment or segments (terga). Also used to describe the entire abdominal dorsum or the thoracic dorsal segments of Odonata.) 5 is a bit paler than adjacent terga (Tergum: the dorsal part of an abdominal segment or segments (terga). Also used to describe the entire abdominal dorsum or the thoracic dorsal segments of Odonata.), but "distinctly paler"? The figure for Baetis alius in the paper, as well as a very nice picture posted by Millcreek in the forum here, shows that Baetis alius would have darker tergites (

One tergite of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.
Couplet 11. The length of the gills is obviously less than 2X their width. This leads to the Baetis vernus complex, which could include that species or Baetis brunneicolor. This key doesn't say how to tell those species apart.
Switching over to Burien et al 2018 as the source, the characteristics used to distinguish vernus from brunneicolor seem to rule out either one. Brunneicolor should have more uniformly brown abdominal tergites (

One tergite of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.
The fore femur (

The femur of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.
Also worth noting: In the genus ID, I thought I could see the villipore in my microscope, but I'm not sure. If I back out of Baetis altogether and assume there's no villipore, I end up at Fallceon, but this specimen doesn't seem to have the frontal keel on the head that's supposed to be present on Fallceon quilleri. So that seems like a dead end as well.
This mayfly was collected from the Yakima River on September 12th, 2020 and added to Troutnut.com on September 19th, 2020.










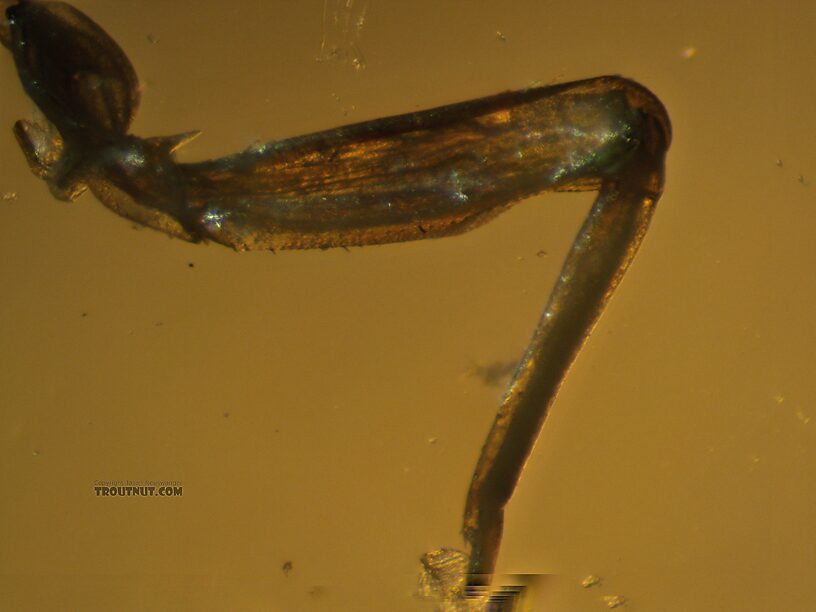
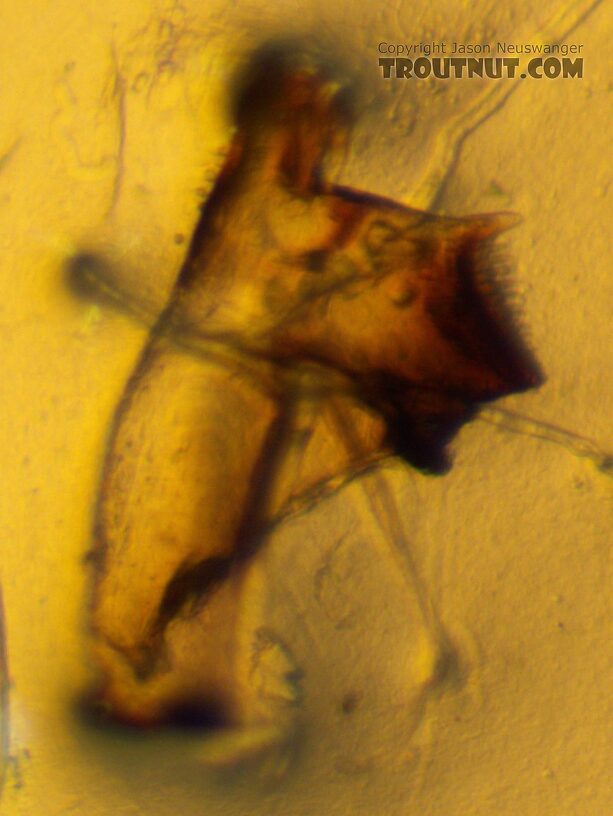
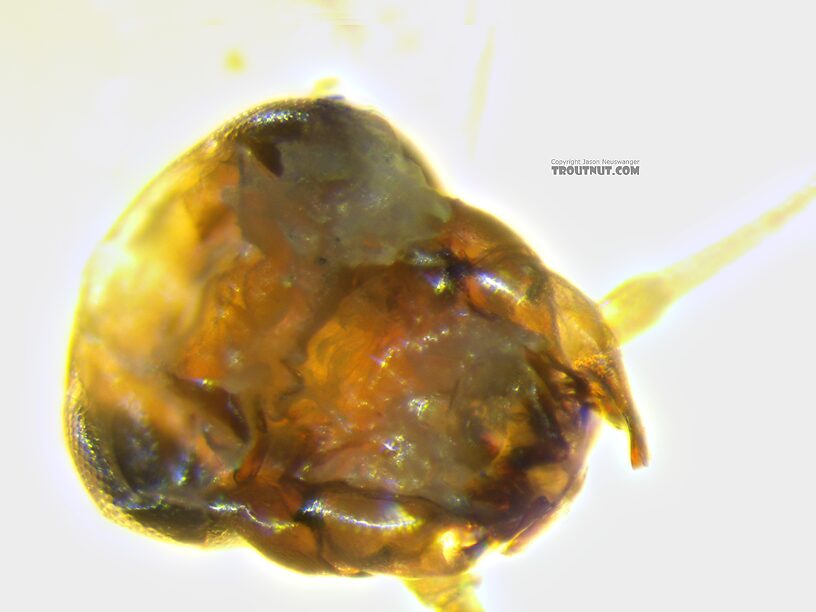
I think the villipore is visible here as a raised area toward the base of the femur on this detached leg, on the side opposite the large setae.



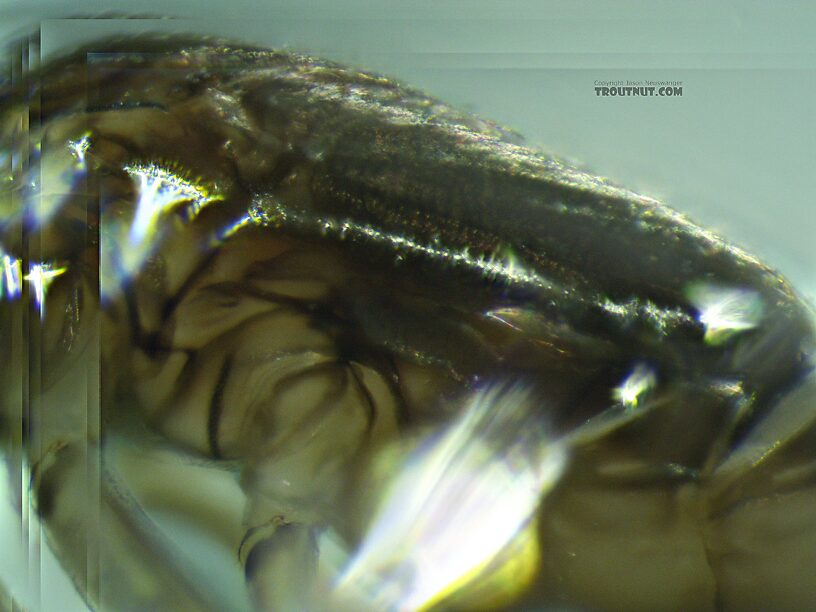
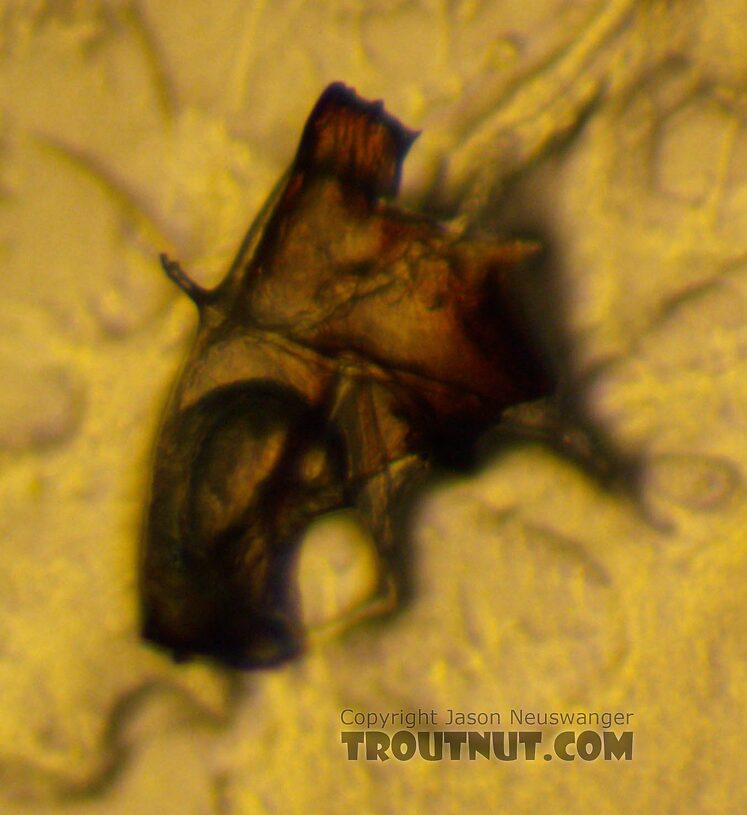
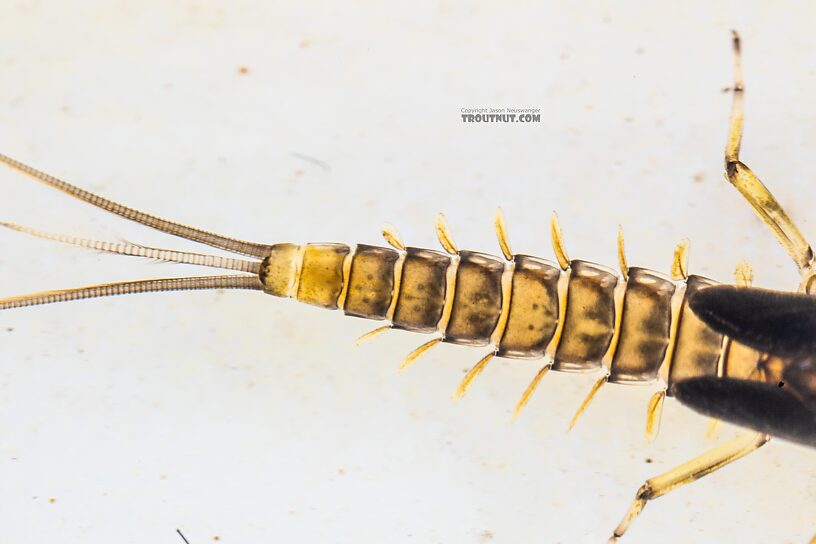
Another gill close-up. I think these are fine and not robust setae?
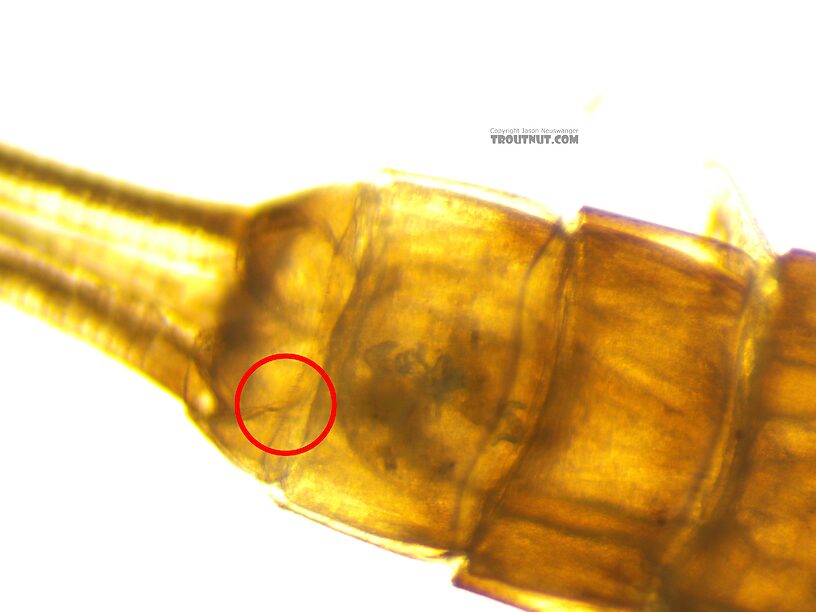
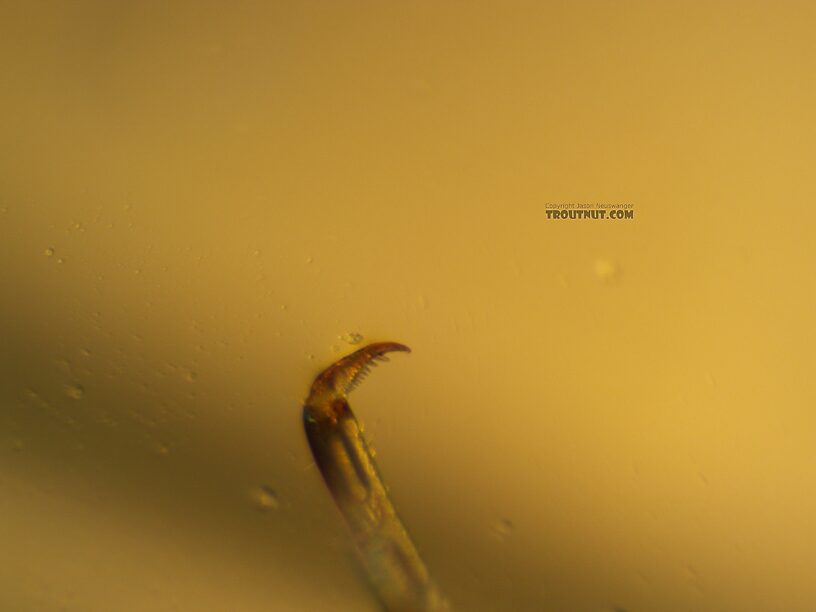
A closeup look at this one shows robust setae along the posterior margin of the 10th tergite. They're a little more clear under the scope than in the picture, but you can see them as short little spikes in the circled area (and a few elsewhere on that margin). I missed these the first time I tried to key this one out, because I didn't realize how subtle and difficult they can be to see.
Recent Discussions of this Nymph
Puzzled on this Baetis nymph ID 2 Replies »
I just added several microscope photos to this specimen and placed in the description my thoughts as I tried to key it out, but I ran into a dead end. Anyone have new insights?
ReplyStart a Discussion of this Nymph:
Top 10 Fly Hatches
Top Gift Shop Designs
Eat mayflies.
Top Insect Specimens
Miscellaneous Sites
Troutnut.com is copyright © 2004-2024 Jason
Neuswanger (email Jason). See my FAQ for information about use of my images.
 privacy policy
privacy policy